Here are some effective methods to immigrate to the United States, summarized from multiple sources:
1. EB-1A (Extraordinary Ability)
For: Individuals with international recognition in fields like science, arts, education, business, or athletics.
Requirements:
Nobel Prize, Olympic medal, or equivalent OR
Meet at least 3 of 10 criteria (e.g., awards, publications, leadership roles, high salary, original contributions) .
Advantages: No employer sponsorship required, fast processing (as quick as 15 days), and priority status .
2. NIW (National Interest Waiver)
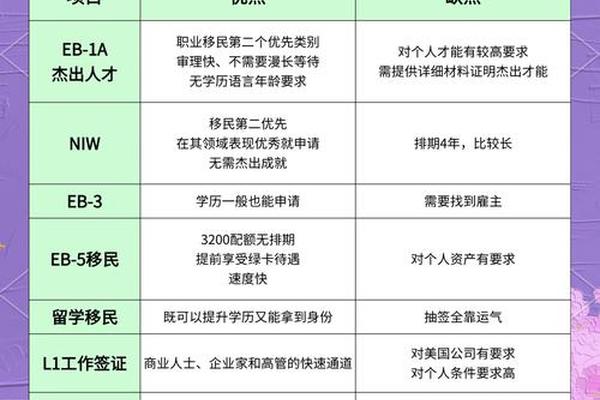
For: Professionals with advanced degrees or exceptional skills in science, technology, or business.
Requirements:
Prove that your work benefits U.S. national interests.
Meet 3 of 6 criteria (e.g., academic achievements, professional licenses, industry recognition) .
Advantages: No employer sponsorship or labor certification needed; slower processing (4–6 years) but lower barriers than EB-1A .
3. EB-5 Investment Immigration
For: Investors willing to contribute to the U.S. economy.
Requirements:
Invest $800,000 in a TEA (Targeted Employment Area) or $1.05 million in non-TEA projects.
Create at least 10 jobs .
Advantages: Fast-track options under the 2022 reforms (no backlog for rural/infrastructure projects), "dual filing" (I-526 and I-485 concurrently) .
4. EB-3 Skilled/Unskilled Worker Visa
For:
Skilled Workers: Professionals with a bachelor’s degree or equivalent experience (e.g., IT, healthcare).
Unskilled Workers (EW-3): No education or language requirements; jobs include farmhands, factory workers .
Requirements: A U.S. employer must sponsor the applicant and prove no qualified U.S. workers are available.
Advantages: Accessible for low-skilled workers but with long wait times (6–8 years for unskilled category) .
5. Family-Based Immigration
For: Immediate relatives of U.S. citizens or green card holders (spouses, parents, unmarried children under 21).
Requirements: Sponsor must be a citizen or permanent resident; some categories have annual quotas and long wait times (e.g., siblings: 10+ years) .
6. EB-1C (Multinational Executive/Manager)
For: Senior executives or managers transferred to a U.S. branch of their company.
Requirements: At least 1 year of employment in a managerial role abroad; the U.S. employer must be operational .
7. O-1 Visa (Extraordinary Ability)
For: Temporary work in the U.S. for individuals with exceptional achievements (e.g., artists, researchers).
Requirements: Similar to EB-1A but for temporary residency; requires employer sponsorship .
Key Considerations for 2025:
Policy Changes: Potential tightening of immigration rules under new administrations, especially for family-based and asylum categories .
Priority Dates: Check visa bulletins for backlog updates, particularly for EB-3 and NIW .
For detailed eligibility assessments or application steps, consult immigration attorneys or agencies like Max Global Immigration or ABC Dream .




